Analysis
Denitrifier-Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry Method
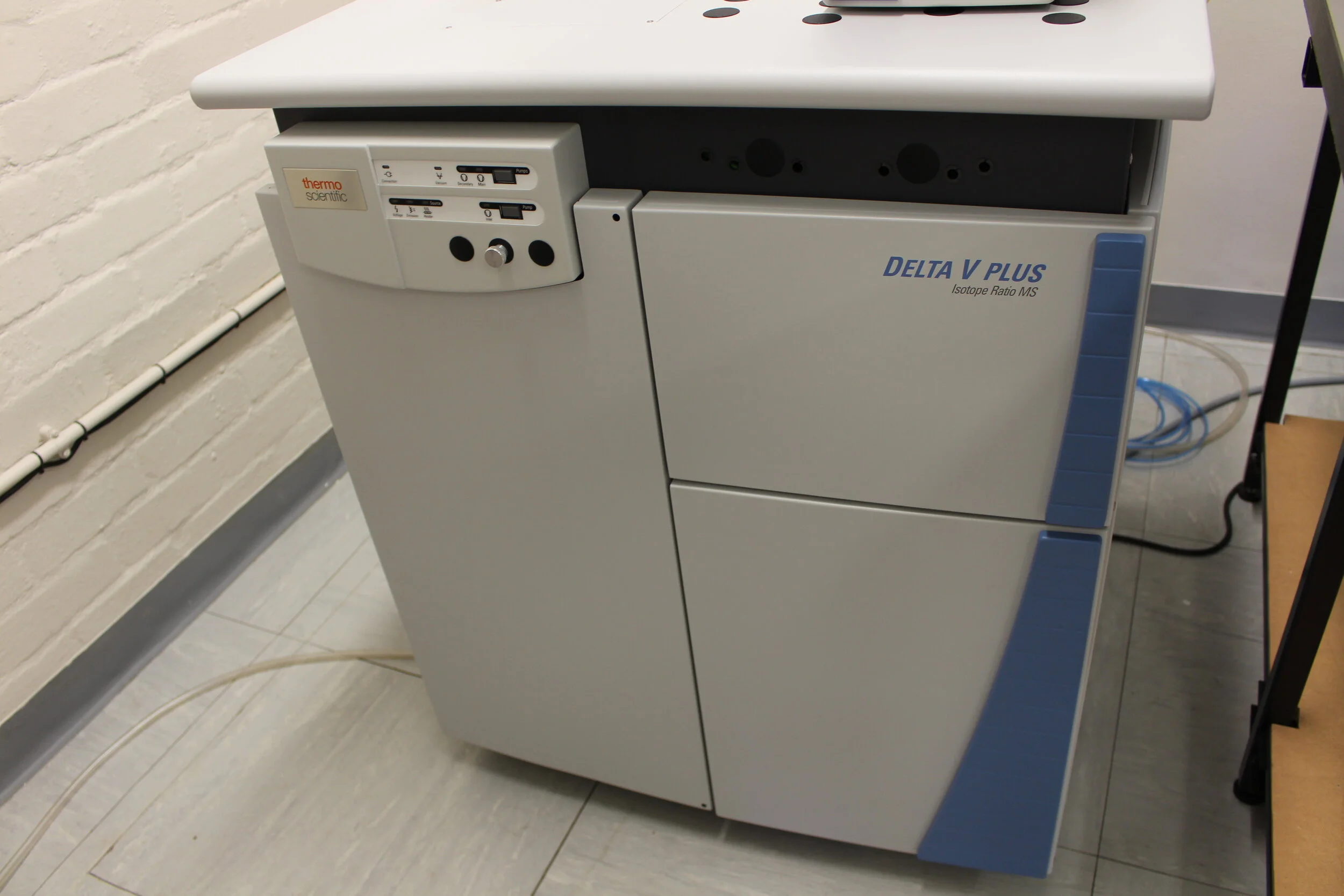
The UCT-MBL has a Thermo Scientific DELTA V Plus Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer (IRMS) equipped with a continuous flow (ConFlo IV) system and custom-built gasbench (including autosampler). The IRMS and peripherals, funded by an NRF National Equipment Programme Grant, the UCT Research Council, and the Royal Society, are used for the analysis of the nitrogen (N) and oxygen (O) isotope ratios (δ15N, δ18O) of N2O gas. The primary purpose of this set-up is not to analyze naturally-occurring N2O gas, although it is possible to measure naturally occurring N2O via this approach. Rather, almost all N species can be converted to N2O by chemical or biological methods, such that the configuration can be used to measure the isotopes of almost all N species. We primarily use the denitrifier-IRMS method, which involves the quantitative conversion of nitrate to N2O gas by facultative denitrifying bacteria that lack an N2O reductase enzyme. The produced N2O, which is measured by IRMS, has a δ15N that matches and a δ18O that is strongly correlated with that of the initial nitrate. The persulfate oxidation method is regularly used in the UCT-MBL to convert organic nitrogen (particulate and dissolved) to nitrate. N2O is uniquely suitable for high-sensitivity isotopic analysis because it occurs at trace levels in the atmosphere, which minimizes contamination, and can be captured cryogenically, which yields a high effective sensitivity.
Nitrate (or nitrite) concentrations of 2 μM to 1 mM can be reliably analyzed using this method.
Nutrient Laboratory
The UCT-MBL is equipped to measure macronutrient concentrations in freshwater and seawater. We have a Channel SEAL Autoanalyzer (AA500) for the analysis of dissolved nitrate, silicate, phosphate, and nitrite. We can also measure nitrate and nitrite via chemiluminescence using a Teledyne T200U Chemiluminescence NO/NO2/NOx analyzer – this approach is particularly useful for small-volume samples, high-concentration samples, or samples with complex matrices (e.g., high viscosity, high/low pH). Ammonium concentrations are analyzed manually using the fluorometric method (Turner Designs Trilogy fluorometer with UV module), while urea is measured spectrophotometrically (Thermo Scientific Genesis 30 Visible spectrophotometer).
Typical concentration ranges that can be reliably analyzed are as follows: nitrate: 0.1 μM to 1 mM; silicate: 0.1 μM to 200 μM; phosphate: 0.05 μM to 10 μM; nitrite: 0.05 μM to 1 mM; ammonium: 0.02 μM to 10 μM; urea: 0.03 μM to 10 μM.
Chlorophyll-a concentrations can also be measured in the UCT-MBL using the non-acidified fluorometric method (Turner Designs Trilogy fluorometer).
Ambient Ion Monitor-Ion Chromatograph
The Ambient Ion Monitor-Ion Chromatograph (AIM-IC) is an instrument that provides simultaneous hourly measurements of the water-soluble chemical composition of atmospheric fine particulate matter and the precursor gas-phase species. The sampling assembly combines a parallel-plate wet denuder for collecting soluble gases, and a particle supersaturation chamber for collecting aerosol particles, thus the aerosol- and gas-phase species are measured simultaneously. The gas and aerosol sample streams are solubilized and pumped to the IC for cation and anion analysis. The instrument is designed to be operated in the field (e.g., at the Cape Point GAW tower or on the R/V SA Agulhas II), and can be left to run continuously for 14 days at a time. In sum, the AIM-IC developed by URG provides real-time direct measurements of nitrate, sulfate, nitrite, phosphate, chloride, ammonium, sodium, calcium, potassium, and magnesium in ambient aerosols, and at the same time, gas phase hydrogen chloride, nitric acid, nitrous acid, sulfur dioxide, and ammonia. The ICs are also used in offline mode to analyze the major cations and anions collected on aerosol filter samples.
TOC/TN Analyzer
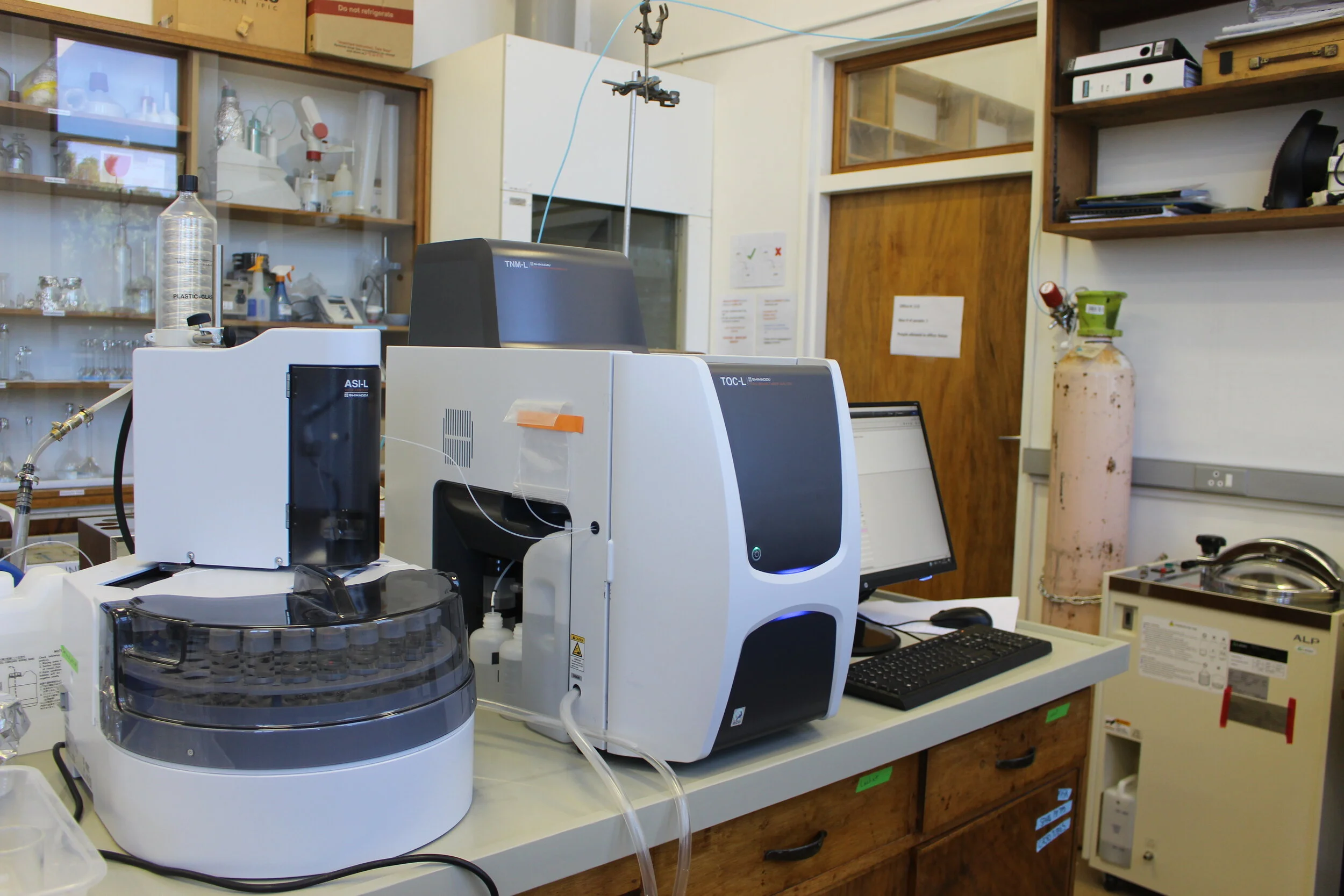
The Shimadzu TOC-L high-sensitivity model equipped with a TNM-L module and autosampler is capable of measuring total organic carbon (TOC) and total nitrogen (TN) over a wide range of concentrations. Aqueous samples (fresh or saline waters) are acidified and sparged to remove inorganic carbon and the remaining sample is then combusted to 680°C in an oxygen-rich environment. The CO2 generated by oxidation is detected using an infrared gas analyzer. The TOC detection limit is 4 µg/L and the full dynamic range extends to 30,000 mg/L. The TN analysis can be performed simultaneously using the 720°C catalytic thermal decomposition/chemiluminescene method. The TN method detection limit is 0.05 mg/L TN and the full dynamic range extends from 0.2 to 500 mg/L. Currently, the TOC/TN analyzer is used primarily for aerosol extracts and seawater samples. The TOC/TN analyzer is part of the BIOGRIP node for Atmospheric Biogeochemistry.
NOx Analyzer ("NOxBox")
A Teledyne T200U Chemiluminescence NO/NO2/NOx Analyzer with custom-built preparation system and SRI PeakSimple data acquisition system allows for the determination of nanomolar quantities of nitrate+nitrite, nitrate-, or nitrite-only in various types of environmental samples (e.g., seawater, freshwater, precipitation, atmospheric aerosol extracts, pore waters, oxidized particulate or dissolved organic nitrogen (N)). Using a custom-built preparation system, sample nitrate and nitrite are reduced to nitric oxide gas (NO(g)) in a hot (95°C), weakly acidic vanadium(III) solution. The NO(g) is transferred to the analyzer in a stream of inert Ar gas where it reacts with ozone (O3) to produce a chemiluminescent flash that is converted into a digital signal indicative of the sample N concentration. The advantages of using a NOx analyzer for N species determination include: i) immunity to matrix effects because sample N is converted to gas; samples of virtually any pH or salinity can thus be measured, ii) tiny volume requirements (as low as 50 µL) such that samples containing minute quantities of N (< 5 nmols) can be analyzed, iii) the analyzer is compact and sturdy enough to facilitate shipboard use, and iv) analytical rates of ~10-12 samples per hour are easily achieved.
Nitrate (or nitrite) concentrations of 0.02 μM to 100 mM can be reliably analyzed using this method.